Orofacial Granulomatosis
Frequently Asked Questions
This document has been developed by ASCIA, the peak professional body of clinical immunology/allergy specialists in Australia and New Zealand. ASCIA information is based on published literature and expert review, is not influenced by commercial organisations and is not intended to replace medical advice.
For patient or carer support contact Allergy & Anaphylaxis Australia or Allergy New Zealand.
![]() ASCIA PC Orofacial granulomatosis 2024122.63 KB
ASCIA PC Orofacial granulomatosis 2024122.63 KB
Q 1: What is orofacial granulomatosis?
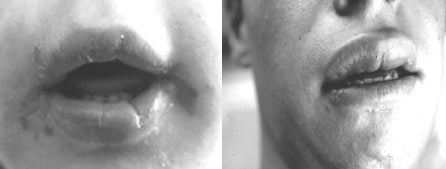
Orofacial granulomatosis (OFG) is a rare skin condition that causes swelling of the lips, mouth and face. It can develop on its own for no known reason (idiopathic OFG) and affects people at any age but is more common in adults. It is not completely known what causes OFG, but it is thought to be related to a bacterial or fungal infection, or an allergy or sensitivity to certain foods or preservatives. OFG also occurs in people who have disorders that affect the immune system.
In OFG, clusters of white cells called granulomas form in the soft tissue in and around the mouth, and in particular, the lips. The granulomas can go away on their own, but in some cases they last for weeks or months and can cause pain and discomfort.
OFG is often linked with inflammatory conditions including Melkersson-Rosenthal syndrome, Cheilitis Granulomatosis, and Schuermann's Glossitis Granulomatosa.
Q 2: Is lip swelling the most common sign of orofacial granulomatosis?
Lip swelling is common in OFG and may only last a few hours at a time at first. This often makes it difficult to distinguish from another type of lip swelling known as angioedema. As the condition progresses, swelling tends to last for days at a time, eventually becoming permanent. The lips may also start to feel firm or ‘rubbery’ and the skin becomes cracked, dry and painful.
Other symptoms of OFG include:
- Swelling of the face, eyes, cheek and/or gum.
- Development of deep grooves on the surface of the tongue (fissures).
- Facial numbness or paralysis.
- Mouth ulcers and inflammation of the gums (gingivitis).
- Tongue swelling or a sensation of a burning tongue.
- Dry, red peeling skin around the mouth.
Q 3: How is the diagnosis of orofacial granulomatosis confirmed?
There are many causes of lip swelling so it is important to rule out diseases or disorders that may look like orofacial granulomatosis. Specialised tests such as blood tests, taking a small sample of the swollen tissue (biopsy), or x-rays will help your doctor diagnose and treat the cause of swelling.
Q 4: How is orofacial granulomatosis treated?
The swelling caused by OFG may resolve on its own without treatment. In most cases, swelling persists for many years. While there is no cure for OFG, several options are available to help manage the disease symptoms. These include elimination diets, medications that reduce inflammation, radiotherapy, or plastic surgery.
© ASCIA 2024
Content updated June 2024
For more information go to www.allergy.org.au/patients/skin-allergy
To support allergy and immunology research go to www.allergyimmunology.org.au/donate